Reading report week 4: Li Zejun (M1)
Chapter 2: Expanding opportunities part 1 (Page 100 ~ 118)
Chapter 6: Global cooperation part 1 (Page 292 ~ 317)
Chapter 2: Expanding opportunities part 1
Summary:
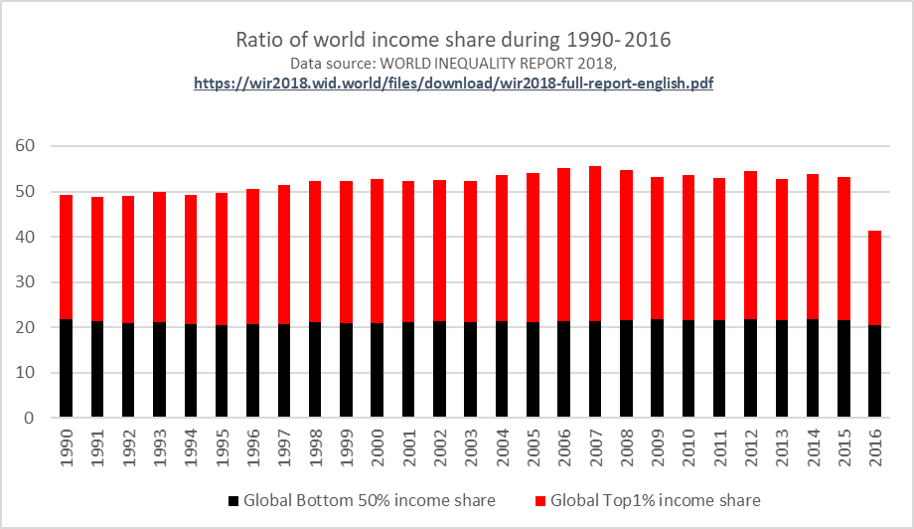
Through the rapid development of advanced technology, it ties entire world closely than we had imagined before. Thanks to Information and Communication Technology (ICT), some kinds of vocations such as streamer and Youtuber born during the blooming period, and they are catching young’s sight gradually. ICT is brings digital dividend enormously at the meantime, it solved inequality in a quite low efficiency. In accordance with “Ratio of world income share during 1990- 2016”, we notice the share of Global Top 1% accounts for 30.65% averagely, comparing with 21.23% of the Global Bottom 50% Group, the ratio of income inequality seems to remain stable after internet innovation. Why cannot internet make more contribution? Why does not digital dividend reduce the poverty? Maybe we can answer them after reading this report.
(Permission was obtained from World Inequality Lab. to use the figure above.)
ICT has ability to create thousands of jobs of relatively good salary and augment human capital to improve the worker productivity in Internet area , meanwhile the people in insufficient infrastructure fail to benefit owing to various problems. Therefore how to balance technology and required skills through ICT becomes critical to estimating inequality . We will explain relation between digital technology and human capital from four aspects : connect people, create jobs, boost to labor productivity and benefit customer.
2.1 Connect People
-Simple phones with limited potencial and the digital divide persists.
 According to present report, averagely 8 in 10 people in the developing countries own a mobile phone. Low price and simple procedure lead simple mobile become superior choice among poor people. Such simple phones can be shared and prepaid immediately, enables the poor to connect other people anytime, therefore become technology of choice. They fail to benefit digital dividend maximally because of simple phones without internet service. Unfortunately in Ethiopia, Cameroon, Rwanda, Tanzania, and Uganda, above 80% of users have simple phones, not capable of browsing the internet and improving quality of life.
According to present report, averagely 8 in 10 people in the developing countries own a mobile phone. Low price and simple procedure lead simple mobile become superior choice among poor people. Such simple phones can be shared and prepaid immediately, enables the poor to connect other people anytime, therefore become technology of choice. They fail to benefit digital dividend maximally because of simple phones without internet service. Unfortunately in Ethiopia, Cameroon, Rwanda, Tanzania, and Uganda, above 80% of users have simple phones, not capable of browsing the internet and improving quality of life.
In spite of rapid spread of digital technologies, more than 800 million people lack mobile access worldwide, and 4.3 billion lack internet access. Enormous gaps remain by income, age, location, and gender. In African countries, the bottom 40 percent is only one-third as likely to have access to the internet as the upper 60 percent; 18 percent of men report using the internet versus 12 percent of women, and 20 percent of youth versus 8 percent of those more than 45 years old. It indicates that inequality to access and obstacle to productive use. It mentions Cameroon, Ghana, Kenya, and Uganda, more than three in four users still access the internet in commercial internet cafes, where high costs and slow connections limit use, which could also impact other users’ experience.
From standpoint of countries, it is tough to improve the ICT particularly without concerning about reality, it conflates the economic issue, policy, infrastructure, etc. However it brings the opportunity for the education companies and mobile manufactures. “How to teach people using smart phones and train skilled workers to maintain service”, “how to design the smart phone that everyone could control it in minutes with appropriate price”, the two questions deserve to be considered and challenged further.
2.2 Creating Jobs
ICT is an effective pill to reduce poverty under precondition.
Digital technologies promote inclusion by boosting employment and earnings in the ICT sector or in ICT occupations across the economy. But most important, they support jobs and earnings in sectors that use ICT when firms and the self-employed adopt new technologies and grow, as well as through ICT-enabled outsourcing and entrepreneurship.
ICT-related companies offer the comparatively limited jobs of world due to high entry barriers, and remains male dominated. The ICT sector employs, on average, 1 percent of the workers in developing countries. ICT occupations— such as network administrator and electrical and electronic engineer—are also 1 percent of employment in developing countries, and 2–5 percent in member-countries of the organization for Economic Co-operation and Development (OECD). Meanwhile the median hourly earnings in the ICT sector and in ICT occupations are 1.5 times higher than in urban non-ICT sectors or non-ICT occupations in developing countries. In addition, ICT sectors induce additional jobs including services as retail, cleaning, and food preparation with low or middle skill, which could serve them better.
In terms of owner site, expanding business by using ICT becomes common recently. Digital technology can increase aggregate employment and income by improving productivity and boosting firms’ economic growth. An estimation that one in four jobs of the United States has already been offshore or could be offshore in the future. These jobs fell mostly into business processing, including call-centers and book-keeping. In addition, ICT enables entrepreneurship to set up e-commercial company and achieve self-employment. As online commerce, the on-demand or sharing economy is growing rapidly, if still small overall and just emerging in developing countries. More than two-thirds of internet users globally are willing to be part of the sharing economy. These new jobs in the sharing economy have advantages for low or middle-income people who plan to get additional income.
2.3 Boosting labor productivity
Digital technology provides platform on which unlimited potential remains.
Digital technologies can complement human capital, allowing workers to focus their efforts on activities with higher value and making them more productive. Farmers can use precision agriculture or track livestock. Teachers can use massive open online courses (MOOCs) or online teaching tools to risen up efficiency for dedicating more time to children who fall behind.
Researchers can dedicate more time for thinking and innovating rather than spending time searching for information or duplicating other people’s work. Managers can work more easily with teams across borders.
It also provide a platform without gender discrimination. Through this report, it is found that the people from low-and-middle income countries are keener to get tertiary education than others who are from high-income countries. What is more? The overall women’s motivation also is higher than men’s! Regarding causal relation of “education- skill (career) – salary” in a common sense, we can utilize digital technology to reform the education platform focusing on potential female customers aiming to rise average education level and mitigate inequality of income and gender.
Except the potential ability to eliminate gender discrimination, ICT is particularly promising to the weak groups such as the poor, women, minorities, the disabled, and people in distant regions. For all of them, high search costs, long distances, and a lack of information are key obstacles. ICT aids them to overcome barriers and earn money by offering online recruitment platform, it is especially efficient in developing countries. Simplifying procedure of recruitment, shortening distance between managers- workers, providers- clients, share latest information, there are still more potentials remaining unrealized in market.
2.4 Benefiting consumers
Various benefits and over connected world.
 To consumers, it benefits lots of aspects to individuals as consumers, such as expanded choice, better quality leisure time, and access to more knowledge, and these benefits are consumer surplus, which are not often captured in GDP statistics.
To consumers, it benefits lots of aspects to individuals as consumers, such as expanded choice, better quality leisure time, and access to more knowledge, and these benefits are consumer surplus, which are not often captured in GDP statistics.
The rapid adoption of digital technologies speaks for itself in spite of high cost. In developing countries, 5 percent of consumption goes into ICT, ranging from 2.8 percent in the poorest households to 6.6 percent in the richest. However there are concerns about loss of privacy, which was mentioned in previous report (check it at “Chapter 4” of previous online book reviewing, http://www.ide.titech.ac.jp/~nabe/wp/online-book-reporting-2/). The problem of “over connectivity” has been recognized since people are constantly online and reachable. The border between leisure and work is blurring. Digital technologies are supposed to make leisure time more enjoyable and less costly, but also make workers more productive and allow them to work away from the office. In fact, more than one-third of internet users in the United States report working longer hours because of technology, despite also feeling more productive. Hence topics, how to re-seperate the life and work under advanced ICT, deserve to be researched from now on.
ICT offfers more probability during serious period.
The COVID-19 prevents us gethering due to its strong infective character, lots of companies decide to introduce telework to continue business. Managers from tradional manufactors to information technology companies, most of them are looking for new meeting type instead of face-to-face. Removing meeting room and utilizing internet communication to improve efficiency, now is acturally becoming common during entrepreneurs. It means more experts will be needed during the popularization of telework during popularization of telework, such as telework manager or data-security keeper. Hence great chance comes to related companies that can treat and send engineers to customers and service them precisely.
COVID-19 is guiding manangers to put their sights on long-term development. It leads (maybe compels) companies to find protential problems in vulnerable condition, encourages them to explore unlimited potentials as well. One apparent advantage of IT companies is that they could adopt new technologies faster than others and modify themselves to maintain service’s quality, which also induces tranditional companies to reform their structure of management forward. In terms of customers, we can select more kinds of goods, services and even a better life in future.
Chapter 6 Global cooperation
The whole countries are facing issues- spam, disease, poverty and pollutants – which are crossing borders and impacting our daily life. These issues could be figured out under people and nations cooperate. The internet is both a subject of cooperation and a complete new tool to facilitate cooperation in other realms. This chapter explores potentials for boosting three forms of cooperation: internet governance, board-cross exchange of goods and service, leveraging the information about sustainable development.
6.1 Internet Governance
Maybe we need a ‘guide’ instead of ‘republic’ currently.
At beginning, the internet was designed as a decentralized network. However the pragmatic libertarian ideology of the internet’s founders is under assault by the commercial and political interests of its other stakeholders, mainly by large corporations and nation-states. The growing commercialization of user data by private businesses and mass surveillance by states, including many sovereigns accustomed to greater state control over their citizens, have gradually eroded the trust the internet once enjoyed. Debate of internet governance appears in below five aspects:
- Power struggle of internet should be a multilateral model(MLM) or multi-stakeholder model(MSM);
- Digital divide diffuses unfairly between developed countries and developing countries;
- Balance between privacy and surveillance concerns;
- Internet is clashing with local cultures and social practices;
- Nonalignment with national policies and regulations.
The first debate is actually basic and capable to lead the blueprint of internet. Internet governance features are characterized by a multilateral system incorporating policy, legal, and regulatory framework for information and communication technologies (ICTs). The prevailing model of internet governance continues to evolve to include its key stakeholders. Through this report, we know the option of MSL receives more support than others, people prefer internet governance under MSL and third party such as IT companies and UN than government.
However, I think we need to rethink to choose MSM or MLM, which mode should be introduced at present. During breakout period of covid-19, as a section of society, the internet need to spread instructors from government by quick decision. Particularly, governance should takes responsibility which includes coping with chaos internet surrounding during an emergency period. As summary, appropriate surveillance could not only maintain entire social system safe but also keep the whole social productivity anytime.
6.2 Board-cross exchange of goods and service
Internet transaction needs supervision to find a better way
Digital goods enable developing country citizen to enjoy the same products in global market. Digital transactions will continue to increase as the number of goods and services offered online increases. For example, with the introduction of online music stores in many developed countries in 2004, digital music started to gain a share of global music sales—from 2 percent in 2004 to 46 percent in 2014. “Spotify”, the Swedish popular media service provider which lunched in 2008, appeals 286 million active users per month, including 130 million paying subscribers. Access to a global market can be particularly advantageous to firms in small, island, and landlocked countries, as well as for countries with small populations, where the size of the local market is often constraining growth.
In addition, the board-cross data has increased economic efficiency and productivity by improving welfare and raising standards of living. As standpoint of firms, they move data internationally to control and coordinate their international operations, maintain an efficient supply chain, and manage human resources, production, and sales to create values. The data can range from personal information about employees and customers to production and technical data. Regarding uncertainty of data management, to treat companies fairly, and prevent national property from Cyber Attacks, lots of government is seeking substitution without setting barriers. At least, countries should enact data protection regulations following internationally recognized principles so that multinational companies do not need to avoid the country because of uncertainty about compliance and trust in the handling of data
6.3 Leveraging information for sustainable development
Balance input and efficiency at a whole world, aiming to build a global platform.
Thanks to internet technology, we could unit donors, development agencies, nongovernmental organizations (NGOs), and international organizations to face two of the world’s greatest challenges: eliminating global poverty and heading off planetary environmental. The costs of these actions are in the trillions of dollars, making global cooperation essential. Primarily they can use digital technologies to deploy funds and knowledge more efficiently and to include more people in the process. They can do so in three ways:
- Getting wired for feedback. Improving the quantity and quality of feedback on internet becomes possible. Past feedback has been thin, slow and unreliable. Technical barriers have been overcome. However such innovation touched organizational inertia, the procedure is still slow and costive. Digital technologies facilitate monitoring of outputs and outcome results, provides this information in a comprehensible aspects. Besides, consistent with privacy considerations, it is important to have an independent group assure integrity of the data system.
- Taking information to scale. Utilizing emerging opportunities to build more efficient and inclusive internet. When information is an input of individuals, we provide costless service to make it benefit everyone in as much as possible, hence information becomes dramatically cheaper and clear; when information is an input of managing complex systems such as power utilities, urban transport, etc. With better information and analysis, these systems can be designed and managed for greater efficiency. In poverty reduction area, the information is treated as input of efforts. It is useful to diagnose challenges and track progress to make policies precisely.
- Mustering information for global public goods. The conception comes from (2), and extend itself to global scale. When we challenge global issues such as climate change, ozone depletion, air pollution, the information is itself a public goods. For instance, the data of solar radiation collected by New Energy and Industrial Technology Development Organization (NEDO). But poor countries do not own enough network of observation stations due to shortage of fund and technology or escape from supervisor of environment organization. So that it is necessary to deploy fund appropriately and integrate a global standard.
Digital dividend and Sustainable Development Goals.
The inequality is still existing on the world. The aforementioned cases are most related to concrete issues which include gap between income, education time, amount of infrastructure, and usage of mobile, etc. The other invisible gaps could not to be measured easily, such as life expectation or self-satisfaction.
ICT ties the whole world much closer than we had imagined before. At first, ICT provides the platform of free expression. The weak group includes women, children and elder has chance to announce requirement and express themselves. In addition, the minority like LGBT also can participate in discussion. Secondly, a wider and mature job-hunting online system had been constructed over past decades. If a person owns qualification (may not), he or she can find appropriate job soon without limitation of physical distance. Thirdly, ICT itself has potential to complement current market situation by introducing telework system, and let women be capable of handling with housework and work at same time. As one of developed countries, Japan also is providing ICT technologies (e.g. Optical Submarine Cable) to developing countries aiming to mitigate global inequality. Finally, there are enormous needs on the way to SDGs. For example, the monitor system that could guide the pursuit of the SDGs, and the capacity to use those data. There could be opportunities for information technology companies to compete on the area of reusable, customizable open-source software and systems, reducing duplication of efforts, saving costs and improving lives.
Digital dividend and COVID-19
Since December 2019, COVID-19 brought us a giant examination to test us how we react to complicated situation. To prevent spread of virus, local government instructs us that stay home maximumly, and continue the study and work on internet. One professor comes from University of East Anglia concluded that amount of CO2 emission per day has descended by 17% at beginning of Aril because of current pandemic. Contrast to reduction of CO2 emission, the male and female unemployment ratio has been increased to 2.9% and 2.3% separately in 2020. The whole society looks vulnerable when we need to over such barriers.
Regarding recent economic recession, I think we had better to rethink the relationship between ICT and society over last 5 months. Honestly speaking, human beings are still benefiting and sharing digital dividend but forget to testify stability among them. For example, the deployment of monitor. To climate change, to weather forecast, there are kinds of monitor stations built around the world, however few warning were announced from them. Therefore the whole society could drop into panic easily. Improving the existing efficiency of monitor system rationally, also becomes critical to the way to SGDs.
As far as I see, an extra criteria that can judge which internet governance, need to be set before emergency comes, which was also mentioned in Chapter 6. No matter how serious the condition is, internet by this criteria could help to maintain productivity, diffuse timely warning in time and predict future precisely. I think now it is the chance to fill blank sector of internet governance and share digital dividend among more people around the world.
Reference:
- World Inequality Lab. (2018). WORLD INEQUALITY REPORT 2018. Retrieved May 2020. From World Inequality Database
https://wir2018.wid.world/files/download/wir2018-full-report-english.pdf
- World Economic Forum (White Paper). (April 2018). Retrieved May 2020. Financing a Forward-Looking Internet for All. P10
https://www.weforum.org/whitepapers/financing-a-forward-looking-internet-for-all
- 労働政策研究・研修機構:新型コロナウイルス感染症関連情報 新型コロナが雇用・就業・失業に与える影響 完全失業率. 独立行政法人労働政策研究・研修機構 2020.05.(参照2020-05-31)
https://www.jil.go.jp/kokunai/statistics/covid-19/c06.html
- 国谷 裕子:出されていた警告. 自然エネルギー財団, 05.(参照2020-05-31)https://www.renewable-ei.org/activities/column/REupdate/20200525.php
- 大崎真孝:プラットフォーム思想. 日本経済新聞 06.08 (参照2020-06-09)
https://www.nikkei.com/article/DGXMZO60009990V00C20A6XY0000/