Presenter : Radhitiya Al Furqan
Date presented : December 7th 2022
Part presented : Chapter 5, pg. 158-173
Chapter title : Advancing human development in uncertain times
Presentation
This chapter is included in part 2 of the report which discusses shaping the future in a transforming world. It argues that uncertainty possesses both positive and negative outcomes, and options to address the uncertainty are either to stick to the current situation/ known paths (yield to paralysis) or explore new possible paths. To give a clearer picture, this chapter shows 2 examples of uncertain conditions and how they provide positive outcomes for humanity, which are rapid technological change and COVID-19 pandemic period.
- Rapid technological change
Rapid technological change became one of the “uncertainties” on the development of humanity. The technological change itself affects many aspects of human life, 3 aspects that being discussed are the energy, artificial intelligence development, and synthetic biology.
In the energy field, technological change and development provide us with better and cheaper renewable energy alternatives. Option on renewable energy usage emerges due to the planetary pressure put by humans to improve their well-being. Energy demands for electricity keep increasing especially during the COVID-19 pandemic where online communications become dominant. As seen in figure 1, the majority of renewable energy alternatives showing a declining pattern in the cost to provide it, especially solar PV (89% declining) and onshore wind (70% declining), in the last 10 years. However, the COVID-19 pandemic also affected clean energy development due to pressures on the public and private budgets.
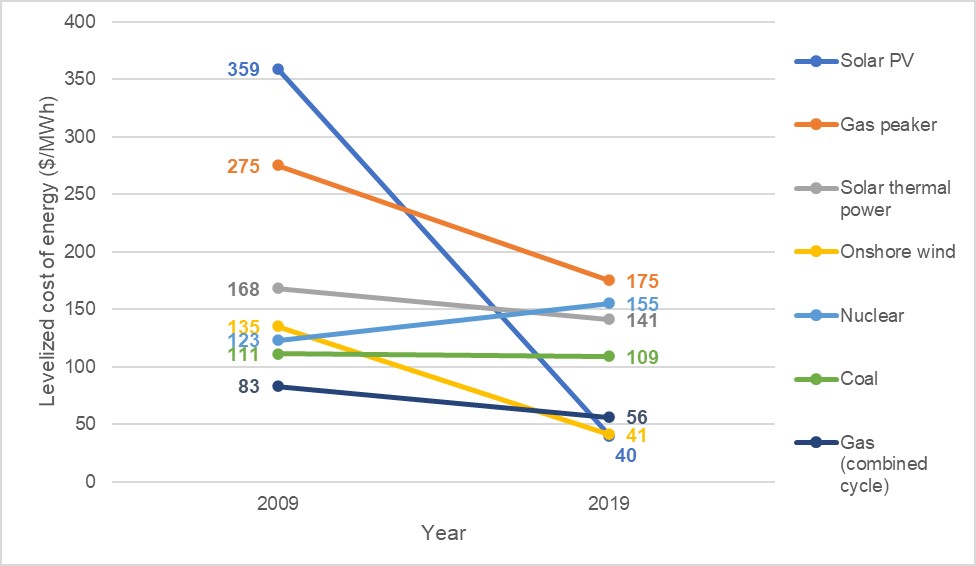
(source: modified from UNDP Human Development Report 2021/2022 according to Roser, 2020)
In the artificial intelligence (AI) field, AI is expected to leverage the demand for labour. It has been a big concern lately with machinery starting to take over human occupations. However, this chapter argues that there is no clear evidence yet that AI completely replaces an occupation. Instead, it is believed that AI could increase the labour demand as AI will open the opportunity to create new occupations. Rather than substitution, a complementary implementation of AI to human jobs is more to be expected (figure 2), e.g. data analysis and decision-making through teaching people cognitive strategies.
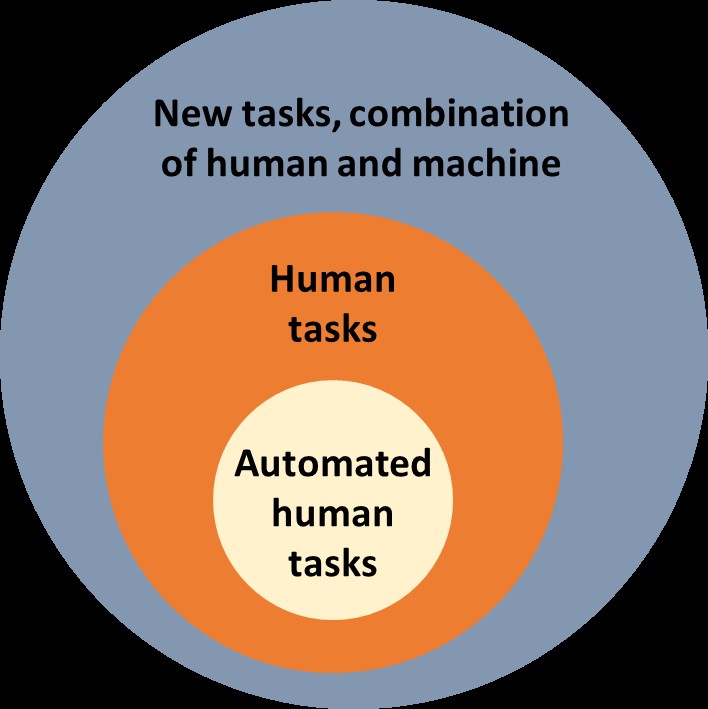
(source: modified from UNDP Human Development Report 2021/2022)
Technological change also rapidly developed in synthetic biology. Currently, we are in an age where biological systems can be re-engineered and redesigned for various purposes. Several fields where biological engineering is implemented include the health sector, agriculture, manufacturing, environmental management sector, and energy sector.
Lastly, rapid technological development did not come without consequences. Several measures need to be considered to balance out the development with ethics and norms. Several implementable measures include; institutional transformation, behavioural transformation, proper incentives, and regulation.
- COVID-19 pandemic period
The uncertainty during the COVID-19 pandemic period was treated as a reflection of where it is possible to make decisions that lead to the development of human life. Three main aspects being discussed are related to technological breakthroughs; improvement in social protection and economic policy; and the alteration of norms and behaviour.
The breakthrough in technology during the COVID-19 pandemic period related to vaccine development. According to the report, the vaccine was introduced only 11 months after the virus’s genetic sequence is published. On the development side, vaccine development showed how multistakeholder collaboration could be carried out appropriately to achieve a common purpose. The collaboration was carried out through the government as the investor; academia as researcher and developer; and industries as mass producers.
The social protection field and economy also made some breakthroughs during the pandemic period. It has been identified in the report that there is an increase in the share of countries that provide health measures from 30% to 100% from the period of January 2020 to July 2022. Country share on monetary support was also provided and increased extremely to almost 90% from January 2020 to around May 2020. The last major improvement that a lot of countries also made is the expansion of affordable internet access, especially considering where school activities were carried out online. Those examples show how a country can provide health and economic support for its citizen during an uncertain period, especially during a pandemic.
Lastly, related to the alteration of social norms and behaviour. Indeed, many social conducts have been altered due to the pandemic, like social distancing, contact tracing, wearing a mask, restrictions on gatherings, and self-sanitizing. And those behaviour are being carried out through a collective awareness and sense of shared responsibility. It shows how people are willingly altering their daily conduct to achieve the common purpose; reducing impact and eliminating the pandemic.
Discussion 1: What kind of job that will most likely to disappear and emerge with the technological development
This question came up responding to the argument about how AI could leverage labor demand instead of declining it. The main concern raises for occupations related to physical labor, for example how programmed machinery will replace human physical labor. However, human labor is still considerably cheaper than machines or AI, at least for now. Hence, even with the current technological development, it is not in the phase where it is available to be mass implemented in economic activities yet.
It was also discussed how technological development will require incentives or improvement on the human side to balance out the situation. In most cases, it is related to skill improvement. Taking an example, in the past, a taxi was a horse-pulled carriage hence less skill was required to become the driver. With the introduction of the automobile and its implementation in the transportation business, taxi drivers must have automobile driving skills, even licensed. This is also expected in the future when perhaps a job will evolve and require humans to develop their skills to carry the job. However, it also needs to be understood that not everyone has the same opportunity to improve themselves or upgrade their skill, hence measures for this issue also need to be considered.
Discussion 2: What things/ behavior that will remain post COVID-19?
As mentioned in the presentation, the COVID-19 pandemic has reshaped many life aspects and social conduct now. One of the simplest points is whether people will keep wearing masks even after the pandemic is over. Some responded they will still wear a mask just to be safe and others will not because of its annoyance. Another one is related to the self-sanitation behavior which has been practiced during the pandemic. Behavior such as using sanitizer and staying away from crowds will most likely remain. It was also discussed that this kind of behavior may remain only in certain generations (e.g. generations that experienced the COVID-19 pandemic) and will disappear in the next generation making them need to adapt again if a similar case occurs, except when the knowledge is passed through the generations.
Reference
Roser, M. (2020). Why did renewables become so cheap so fast. Our World in Data.
UNDP. 2022. Human Development Report 2021/2022, Uncertain Times, Unsettled Lives: Shaping our Future in a Transforming World. United Nations Development Programme. New York.